Lifecycle of Components
The react lifecycle method is used in the React class component. It helps us in creating our state and mutating them.
Each component in React has a lifecycle which you can monitor and manipulate during its three main phases.
The three phases are: Mounting, Updating, and Unmounting.
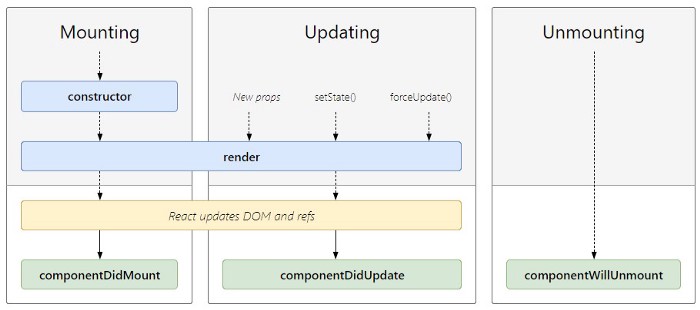
Common lifecycles
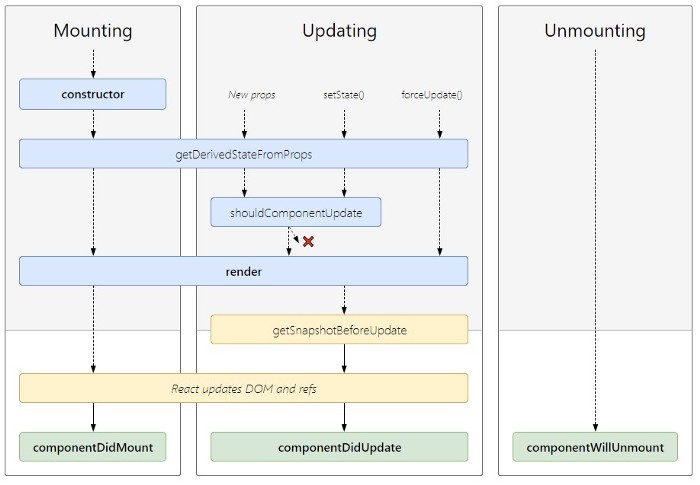
All lifecycle
Lifecycle Hook of Components
Mounting
The mounting means to put elements into the DOM. React uses virtual DOM to put all the elements into the memory. It has four built-in methods to mount a component namely
- constructor() : method is called when the component is initiated and it’s the best place to initialize our state. The constructor method takes props as an argument and starts by calling super(props) before anything else.
- getDerivedStateFromProps(): is called right before rendering the element in our DOM. It takes props and state as an argument and returns an object with changes to the state.
- render(): This is the only compulsory method required by the React. This method is responsible to render our JSX to DOM
- componentDidMount(): The most common and widely used lifecycle method is componentDidMount. This method is called after the component is rendered. You can also use this method to call external data from the API.
Updating
This is the second phase of the React lifecycle. A component is updated when there is a change in state and props React basically has five built-in methods that are called while updating the components.
- getDerivedStateFromProps():
- shouldComponentUpdate(): This lifecycle method is used when you want your state or props to update or not. This method returns a boolean value that specifies whether rendering should be done or not. The default value is
true. - render()
- getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(): This method is called right before updating the DOM. It has access to props and state before the update. Here you can check what was the value of your props or state before its update. So let see how it works.
- componentDidUpdate(): is called after the component is updated in the DOM. This is the best place in updating the DOM in response to the change of props and state.
Unmounting
The final or the end of the react lifecycle is Unmounting. This is used when a component is removed from the DOM. React has only one built-in method that gets called when a component is unmounted
- componentWillUnmount(): If there are any cleanup actions like canceling API calls or clearing any caches in storage you can perform that in the componentWillUnmount method. You cannot use setState inside this method as the component will never be re-rendered.
Summary
- The constructor() method is the best place to initialize our state
- The getDerivedStateFromProps() is a rarely used lifecycle method and is the best place to set the state object based on the initial props.
- The shouldComponentUpdate() specifies whether React should continue with the rendering or not.
- The render() method is the most used and compulsory lifecycle method.
- The getSnapshotBeforeUpdate() method has access to the props and state even after the update.
- The componentDidMount() is the most common and widely used lifecycle method and is called after the component is rendered. You can also use this method to call external data from the API.
- The componentDidUpdate() method is called after the component is updated in the DOM and is the best place in updating the DOM in response to the change of props and state.
- The componentWillUnmount() happens just before the component unmounts and is destroyed and is used for cleanup actions like canceling API calls.